DRYERS
There is one word which every engineer should have in their toolbox - " SIMPLICITY "
The more complicated a piece of equipment or system is, the harder it is to learn, operate and service and generally is considerably more expensive to purchase and maintain.
"SIMPLE IS BEST"
Easy to Learn
Simple Operation
Minimal Maintenance
Cost Effective
CHOOSING THE RIGHT DRYER:
As almost every compressed air system has differences - application, size, location etc. the selection of the correct type of dryer is critical in maintaining the integrity and profitability of the process into which it is installed. There are also limitations on what each of the different dryer types are able to handle and provide, for example temperature, pressure, flow, and required dewpoint etc.
The first point to consider is the quality of air required for the application in which the air is being used. For more information on air quality classifications and recommendations - click here
There are of course some basic considerations, the first of which is the industry or use of the compressed air. This can be simplified:
Plant Air - This is usually air which is used for air tools and general usage, Air quality is not the primary importance.
Instrument Air - This is usually air used to operate valves, actuators, conveyance systems etc. Air quality is important.
Process Air - This is air used in the manufacture of the end product and the air will invariably come into contact with the end
product either directly or indirectly - Air quality is critical.
The basic features, benefits and limitations of the various "standard dryers" will be outlined below.
"Selection of the correct dryer is dependent on several factors"
If you are considering purchasing a new dryer then click on the button, complete the form and we will be happy to send you our recommendations.
Deliquescent Dryer
Deliquescent dryers utilise the principle of absorption , meaning that the desiccant media is affected by the moisture in the air and has to be frequently topped up/replaced.
BENEFITS
- Simple Operation.
- No power requirement.
- Can be used pretty much anywhere.
LIMITATIONS
- Only provides dewpoint suppression.
- Outlet air can be corrosive.
- Frequent replacement of absorbent media.
- Disposal of effluent may be an issue.
Would only recommend this type of dryer for the most basic of compressed air systems, short term use, where high moisture content is an issue but air quality is not the highest consideration.
Generally used for - Plant Air
ONE OF THE SIMPLEST POINT OF USE DRYERS
Membrane Dryer
When coupled with the right filters and drain, this is a great and simple point of use dryer. Basically a molecular filter which uses a porous media that traps the water molecules and allows the dried air to pass through.
BENEFITS
- Simple Operation, no moving parts.
- Little/no power requirement.
- Minimal maintenance.
- Simple installation.
- Can be used pretty much anywhere.
LIMITATIONS
- Limited/small flow capacity.
- Pressure consideration.
- Temperature consideration.
- Disposal of used membrane may be an issue, contaminated waste.
Generally used for - Plant Air & Instrument Air (Point of use, small flow)
THE MOST COMMON OF ALL DRYERS (because it is preferred by General Industry)
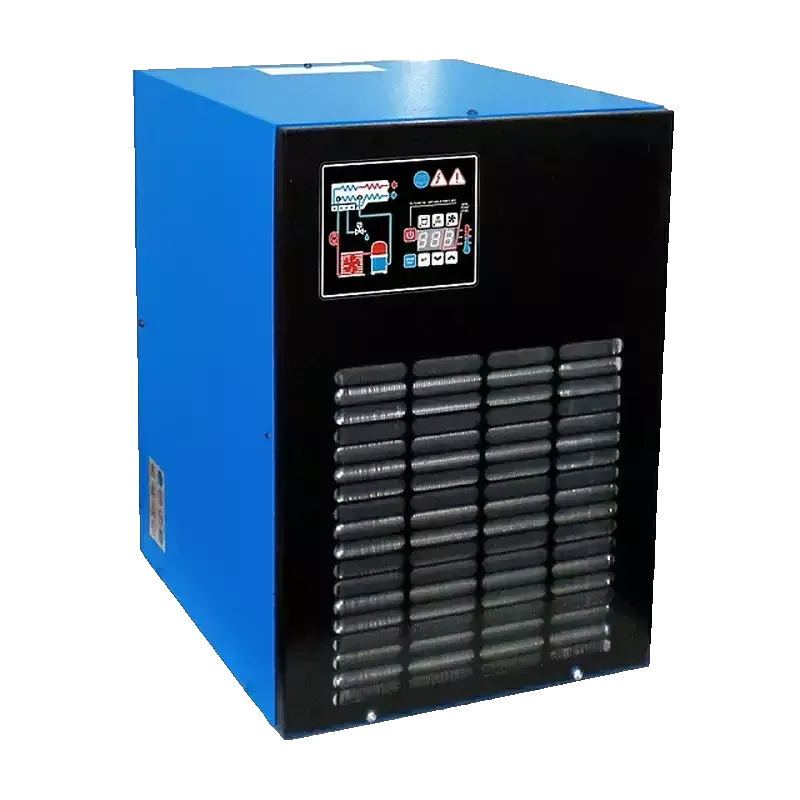
Refrigerant Dryer
A refrigerant dryer works on pretty much the same principle as the fridge in your home. The "hot" compressed air is passed through a hot-cold heat exchanger, where a large percentage of the moisture condenses and then the air is passed through a cold-hot heat exchanger where the "cold" compressed air is re-heated causing it to expand, effectively creating compressed air with a lower R/H.
BENEFITS
- Simple Operation, few moving parts.
- Little/no power requirement.
- Minimal maintenance.
- Simple installation.
LIMITATIONS
- Dewpoint limitation.
- Flow consideration.
- Pressure consideration.
- Temperature consideration.
- Location consideration.
- Refrigerant top ups.
Generally used for - Plant Air & Instrument Air (General Industry)
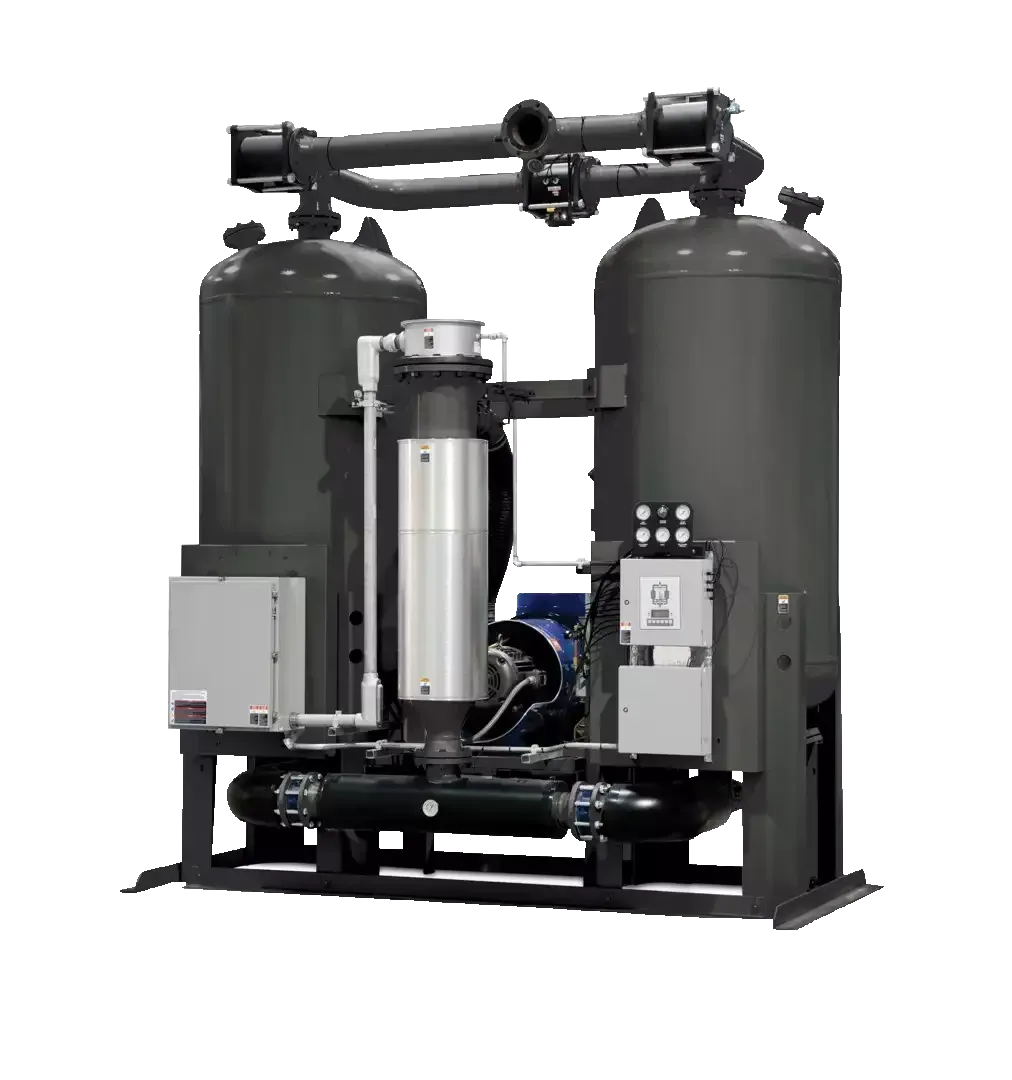
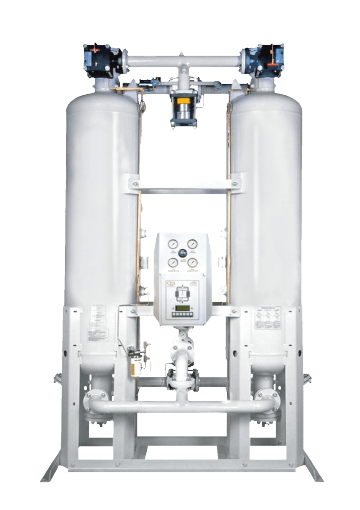
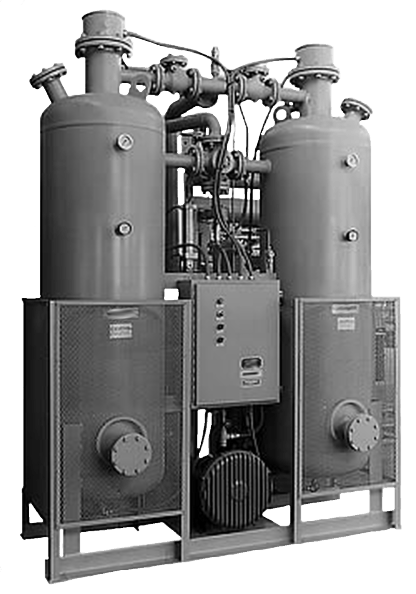
Desiccant Dryer
There are 3 main types of "standard" desiccant air dryer (scroll down)
Dewpoint
Will provide dewpoints as low as -40°C (-40°F) & -70°C (-94°F), providing corrosion protection for most ferrous based systems.
Flexible features
Generally provides all the indications and alarms necessary to operate, diagnose and maintain, without over complicating things
Applications
The only choice for Petrochemical, Chemical, Refineries, Pharmaceutical, Food & Drink - high end processes or where the air is used to and comes into contact with the end product.
Competitive Prices
Don't over complicate the requirement and the value of peace of mind, quality and reliability is fully repaid.
Please enter as much information as possible, if the information is not available then enter N/A, if it is not applicable then enter NAp.
The more information you can provide, the more accurate our recommendations will be and the quicker we will be able to respond.
Guaranteed response within 24hrs.
If you are a subscriber then we will respond within 6hrs. Enter your subs. reference in the additional information section.
Dryer - Recommendations Request
Revenue Streams: Consultancy Retainers, Advertising, Training Courses, Consultancy Fees, Subscriptions, Documentation/Data, Posters/Merchandise - we do not receive any revenue from parts or equipment sales associated with our interaction or recommendations.
The placement of advertisements for products or services within the C.A.D.S. website should not be seen or construed as endorsement of said products or services.